As the global economy continues to evolve, trade and commerce play a vital role in shaping the world we live in. One crucial aspect of international trade is tariffs, which can have a significant impact on businesses, consumers, and the economy as a whole. In this article, we'll delve into the world of tariffs, exploring what they are, how they work, and their effects on global trade.
What are Tariffs?
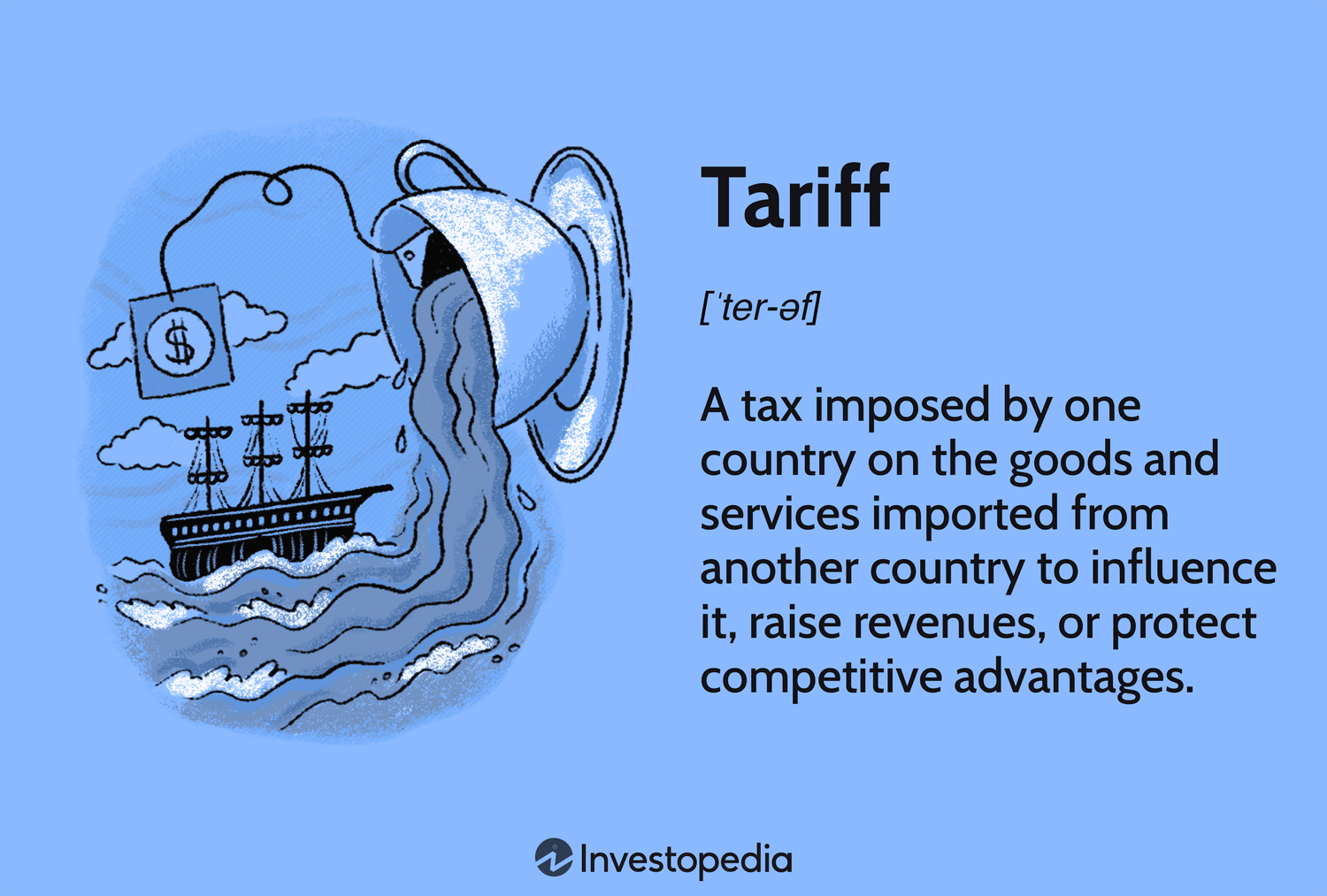
Tariffs are taxes imposed by a government on imported goods and services. They are a type of trade barrier that aims to protect domestic industries by making imported goods more expensive. Tariffs can be imposed on a wide range of products, from raw materials and manufactured goods to agricultural products and services. The primary purpose of tariffs is to generate revenue for the government and to shield domestic businesses from foreign competition.
Types of Tariffs
There are several types of tariffs, including:
Ad valorem tariffs: These tariffs are levied as a percentage of the value of the imported good.
Specific tariffs: These tariffs are levied as a fixed amount per unit of the imported good.
Compound tariffs: These tariffs combine ad valorem and specific tariffs.
Tariff-rate quotas: These tariffs allow a certain quantity of goods to be imported at a lower tariff rate, with higher rates applied to quantities exceeding the quota.
How Do Tariffs Work?
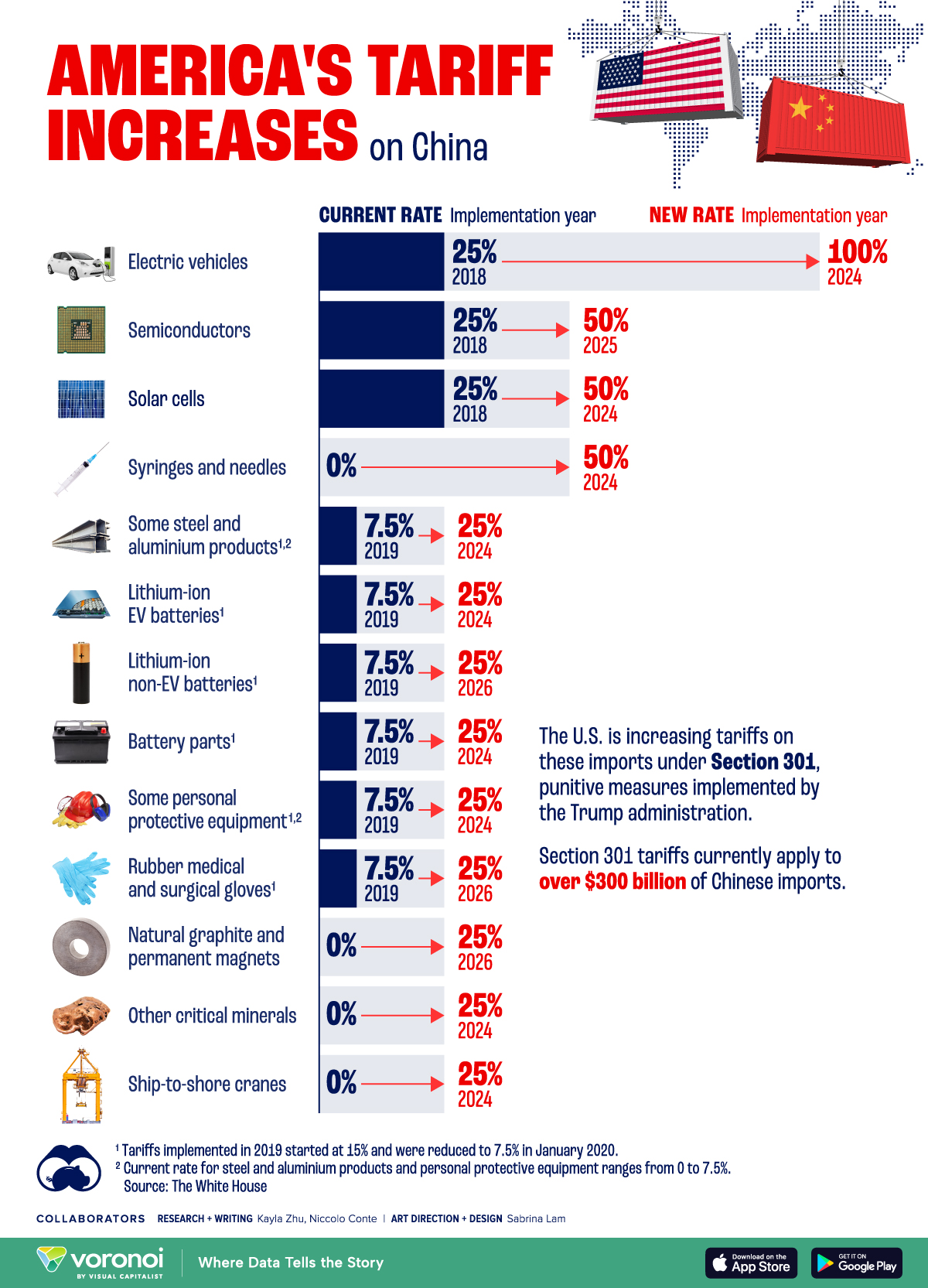
When a country imposes a tariff on an imported good, it increases the cost of that good for consumers. For example, if a country imposes a 10% tariff on imported electronics, the price of those electronics will increase by 10%. This makes domestic alternatives more competitive, as they are not subject to the same tariff.
Here's an example of how tariffs work:
A foreign company exports electronics to a country with a 10% tariff.
The tariff is applied to the value of the electronics, increasing their cost.
The increased cost is passed on to consumers, making the imported electronics more expensive.
Domestic electronics manufacturers benefit from the tariff, as their products are now more competitive.
Effects of Tariffs
Tariffs can have both positive and negative effects on the economy. Some of the benefits of tariffs include:
Revenue generation: Tariffs can generate significant revenue for governments.
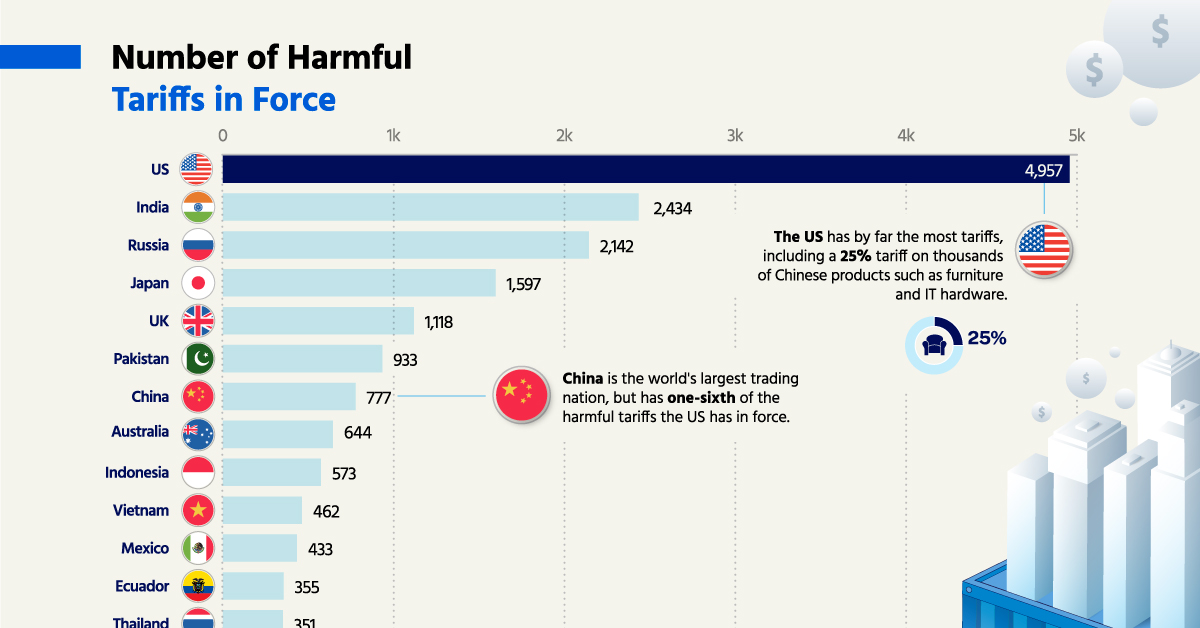
Protection of domestic industries: Tariffs can protect domestic businesses from foreign competition.
Job creation: Tariffs can lead to job creation in domestic industries.
However, tariffs can also have negative effects, including:
Increased costs for consumers: Tariffs can increase the cost of imported goods, making them more expensive for consumers.
Trade wars: Tariffs can lead to trade wars, where countries impose retaliatory tariffs on each other's goods.
Reduced economic efficiency: Tariffs can reduce economic efficiency by distorting market prices and creating trade barriers.
In conclusion, tariffs are an essential aspect of international trade, and understanding how they work is crucial for businesses, consumers, and policymakers. While tariffs can have both positive and negative effects, it's essential to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of tariffs and consider their impact on the global economy. By doing so, we can promote fair trade practices and foster economic growth and development.